
What is Reactive Maintenance
Maintenance is important in keeping your company’s equipment working and performing effectively for as long as possible. It is associated with downtime and cost, so there are times that it is put off and avoided to maximize profit as well as the production of the company. But this neglect can be detrimental and could cause serious damage in the long run. Thus, it is important to have maintenance.
There are two types of maintenance done in companies: planned preventive and reactive maintenance. It is important to distinguish the difference between the two, to know which one your company needs.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Reactive and Planned Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance tackles issues before they occur. This type of maintenance aims to reduce the chances of unexpected equipment failures. It may include cleaning, part replacement, and thorough inspection of the equipment. Doing this type of maintenance detects and corrects problems before they become bigger and more damaging problems.
Reactive maintenance, on the other hand, is a kind of maintenance that is done after the equipment is broken down. This could cost hundreds or thousands of dollars to repair and keep the equipment. In the past, companies would often conduct maintenance in this manner.
Closer Look at Reactive Maintenance
There are times that a building’s equipment such as office dishwashers and office microwaves, and essentials like sinks and toilets would suddenly break down and fail to do their work. This is where reactive maintenance is done.
Reactive maintenance is where the reason for the fault (in case something goes wrong) is immediately investigated and repairs or replacements are carried out. It is sometimes referred to as breakdown maintenance and run-to-fail maintenance. It is maintenance performed and done when the equipment is already broken.
Usually, this type of maintenance involves part replacement or replacement of the machine. Though most of the time, thorough cleaning and removal of dust and other particles solve the equipment problem.
Small reactive maintenance such as thorough cleaning and battery replacements could be done by your regular employees. However, doing reactive maintenance on a bigger scale, such as tackling heavier and larger machines, should be done by specialists.
Advantages of Reactive Maintenance
It may appear that reactive maintenance is full of risks, including the cost. However, there are still a number of advantages of reactive maintenance that you should consider.
Here are the advantages of having reactive maintenance:
- Considering the fact that you only need reactive maintenance during the times when something is broken, or something goes wrong, there will be less labor required. The initial costs of doing reactive maintenance are much lower than that of planned preventive maintenance.
- With reactive maintenance, you get to evade unnecessary preventive measures. This move could save you both time and money.
- There will be no need for equipment or technicians required for routine maintenance.
- No need for planning. With reactive maintenance, planning and scheduling are not essential.
Disadvantages of Reactive Maintenance
Despite the different pros, there are a lot more cons to consider with reactive maintenance.
Here are the disadvantages of having reactive maintenance:
- There will be times that the broken equipment will take more time compared to others. This could cause the operation for a long time. This will bring significant amounts of unplanned downtime that will directly affect the productivity and profitability of the company.
- Some parts that may be required during reactive maintenance may not be readily available. This would cause additional unnecessary delays.
- The cost of reactive maintenance is one of its major disadvantages. Some failed machines could easily be restored to normal function through thorough cleaning and removal of blocks or grits in the machine. But most of the time, for most equipment especially the large ones, that is not the case. Most equipment failures that undergo reactive maintenance require the replacement of parts or the entire machine. Most of the parts are not readily available or expensive to purchase. Some failures even require the hiring of an outside specialist to install or repair the broken-down equipment, thus the additional cost.
- Lastly, reactive maintenance is not known to extend the lifespan of machines. It might even contribute to its shorter life expectancy. When machines are not running in optimal condition for a long time, it can hinder their performance and would likely fail sooner than it would with regular updates and facilitated improvements.
Types of Reactive Maintenance
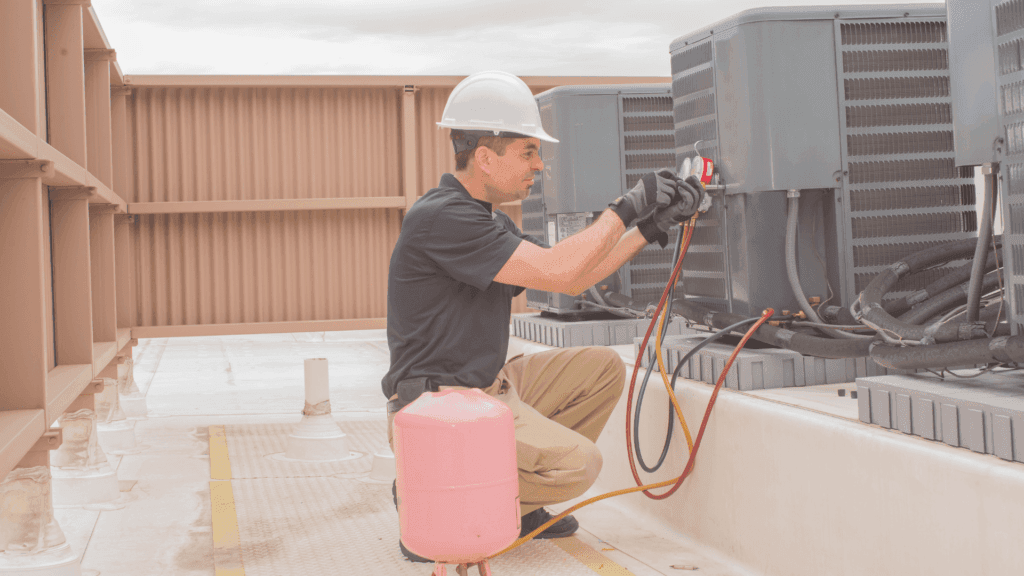
There are three different kinds of reactive maintenance: emergency maintenance, breakdown maintenance, and corrective maintenance.
- Emergency Maintenance
This is a kind of reactive maintenance that is done immediately to keep a machine or an asset operational or for safety issues.
- Breakdown Maintenance.
A kind of reactive maintenance that is done on a repairable machine that has broken down. Maintenance is done to spare the machine from further damage.
- Corrective Maintenance
It is a kind of reactive maintenance that is done on machines with minor issues. If it is seen that there are elements that could be improved or repaired, they are fixed immediately to improve general operations.
When Should Reactive Maintenance Be Used?
At this point, you may have concluded that reactive maintenance is unnecessary and having planned preventive maintenance is a much better choice. Still, there are few situations wherein reactive maintenance remains the best choice. This applies to cases of nonessential equipment.
These failures are:
- those that can be treated or repaired in a short time without the need of a specialist
- does not present a safety risk to the employees
- does not have a big effect on the productivity of the company or efficiency of the workplace
In essence, reactive maintenance could be used on equipment that is non-essential and is an easy fix. Common examples of these are lightbulbs, hand sanitizers, and handheld vacuums.
Takeaway
Having maintenance is a must in every workplace. It is important to keep things working efficiently for a long period of time. It is at the discretion of the company as to what kind of maintenance it needs – it may be reactive or preventive maintenance, as long as it solves the problem.
In selecting the type of maintenance, it is best that you look into the difference between both and find out which is best for the situation your company is in.
For more information about reactive maintenance, contact us.